 |
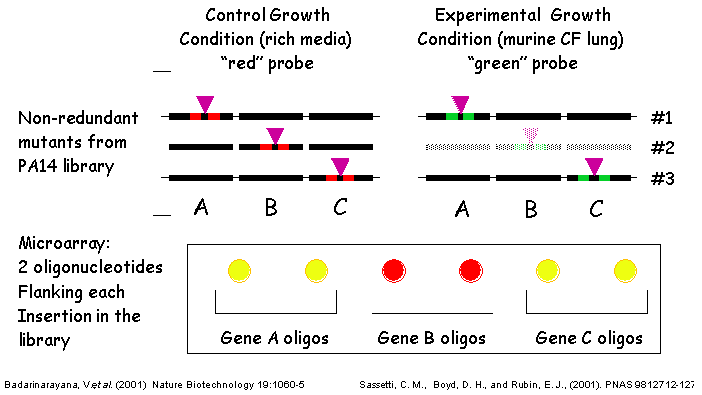
| Figure 6 - TraSH Methodology: Detects the loss of specific transposon mutants from a pool of mutants. In this example, mutant #2 containing a transposon insertion in gene B is lost under experimental selection conditions. Hybridization of fluorescently labeled TraSH probes from both pools of mutants to an oligonucleotide microarray of P. aeruginosa genes reveals that mutant #2 is absent from the experimental pool.These data suggest that the gene disrupted in mutant #2 is important or required for the ability to persist under the given experimental treatment. |